Url looks suss. Seems kinda sophisticated for the usual ups fishing scam. Here’s the text message I got leading here.
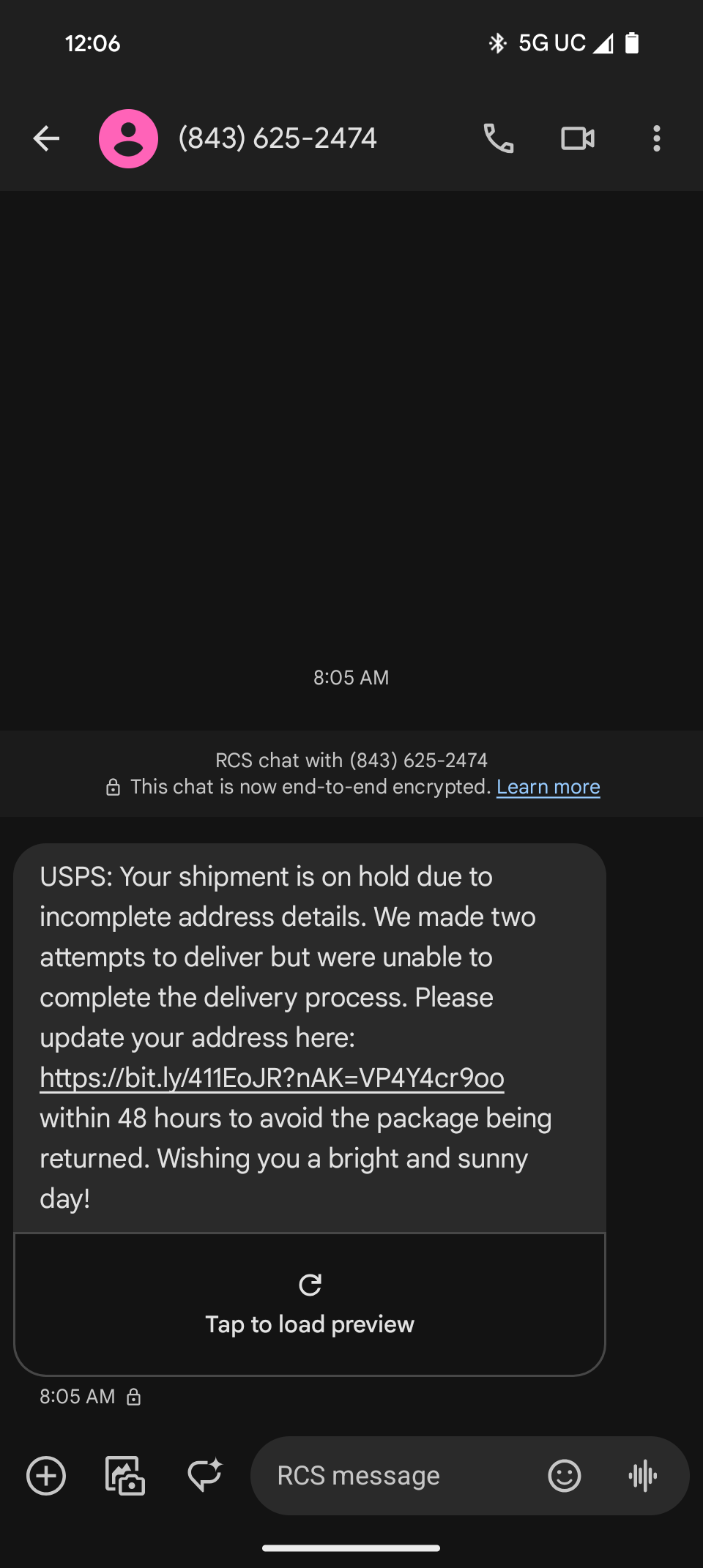
“Wishing you a bright and sunny day!” Lol, I almost want to help this guy by explaining that UPS and American companies in general have disdain for their customers and would never wish them to have anything that would not benefit the company.
I seriously doubt USPS bought a domain like gflrml dot cyou for their business. It’s 300% a scam.
Reminds me of my previous bank.
They changed some system countrywide, so I got an email that I need to update some data and go to a website to do that.
If was something like “update-[bankname]-data-now.tld”.
It was sent to a unique mail address I used for them. But still though it was phishing.
Turns out: No. It was real. Whoever came up with the idea to not host that stuff on at least a subdomain of the bank really needs to get fired. and each and every manager who was part of the decision process.
Ugh. I work in the public sector and let me tell you, there are SO many companies that send the most dogiest, scammiest looking emails telling you to follow a link, only for it to turn out to be perfectly legitimate.
I honestly can see now why people end up falling for these things when even legitimate companies send emails looking just like phishing scammers
Had that happen, too. We all try to educate users to NOT click on some dubious phishing/scams and put in qute some effort to explain it over and over again, and then there are companies doing things like that. It’s just sad.
lol I have to go back to the bank (when there’s a manager, because there wasn’t last time🤦♀️), to turn online banking back on for my account.
It got turned off because I didn’t pick up some spam call they made.
The text message is the big red flag, that’s obviously a scam and has been happening for at least a year. Most scam texts are filtered on my phone, but a few of these slip thru.
I guess they’re just trying to tie phone numbers to addresses so they can sell the phone list for more info.
Especially with people keeping their cell number while moving states, tying an address to the number and verifying it’s that person would be a tidy profit.
Link shortener (not their own at least) is another massive red flag, same with typos (‘number number’ in page)
Unfortunately I can think of one company in particular that uses tinyurl when you sign up for shipping updates on their website (looking at you Samsung!).
At least with that one:
- you know you signed up for it
- they send a text right when you sign up for it
- they use an official short SMS (5 digit) number.
Also, is it common for a legitimate government agency to use a third-party link shortener like bitly?
You mean (uint32_t)-1 %
flip the question around: Why would you think this wasn’t a scam?
Furthermore, wtf did they GO TO THE URL FROM A TEXT MESSAGE at all?! 🤦🏽♂️
FFS, people. There’s “I need help with my computer” and then there’s “Some of us shouldn’t have a smartphone”. 🫶🏼
Holding up a giant sign that says “I CLICK ON WHATEVER BULLSHIT LINK YOU SEND ME”
tbf, it could be sandboxed and safe. I doubt it is, OP doesn’t seem the type, but it could be.
Doesn’t matter, there’s more than likely a callback in the url that says who it was, and now the sender knows the number is active and the user clicks on links
deleted by creator
Even just opening the link can leak info - I would avoid doing so entirely unless your device is sandboxed
deleted by creator
Very well known scam. Some details that give it away:
(1) They used a url shortener that doesn’t let you see the actual domain. (bit.ly)
(2) Website domain is not legitimate.
USPS’s website is usps.com. If the URL doesn’t end in usps.com (meaning usps.fakewebsite.com is still fake) then it’s not legitimate.
(3) Tone: The USPS doesn’t text you like you’re their friend.
(4) The number they’re texting you from is not an SMS short code number (usually 5 digits). Instead you’re getting a text from a 10 digit number with an area code, which means it’s a person/individual rather than an application or service.
source: used to work as cyber sec analyst
(5) grammatical error(s): “We will ship again in” instead of “we will ship again on”
Edit: more subtle errors and phrasing that feels like it was written by a non-native English speaker.
(6) USPS tracking numbers are like 65 digits long, because they expect to track every hydrogen atom in the known universe individually.
Yeah the first bullet copy with the comma and wrong preposition is clearly unprofessional. These scams always use poor contrasting red warning text as well.
I heard a theory that they put mistakes in intentionally to filter for dumb people.
Doubt that’s true, but it’s a funny idea.
It’s absolutely true, they want to make sure the victim won’t realize it’s a scam partway through and bail.
Why would they care though?
If it takes a couple hours to extract money from somebody they don’t want to waste an hour on someone they can’t close.
Scams are still businesses that care about efficiency.
You’re absolutely right, of couse, but keep in mind that communications is still mostly done by people and people are generally fucking stupid.
I’ll add how is it that they could not know the address of the recipient, yet would know their phone number?
Either the recipient is totally unknown or they know the address. The last thing they would know about a recipient is the phone number.
That’s interesting I didn’t think about that fourth point, but whenever I get a verification SMS it does always come from a 5 digit number.
That one is not hard evidence though, for example delivery drivers from FedEx in my area send text messages from their actual phones announcing an upcoming delivery.
The messages are still standardized, so I’m assuming they are company phones and send pre-programmed messages from templates, but if I call that number, I’ll actually speak to the person handling my delivery.
A tangent:
What annoys me is when legitimate companies use non-standard URLs in their hyperlinked emails. For example, if you get a message from Facebook taking you to facebookemail.com, that’s actually a domain controlled by the real Facebook.
They’re essentially teaching their customers to click on links in emails which use unfamiliar URLs which are superficially similar to the usual one.
They probably want to separate their customers from getting up to stupid spammy behaviour and getting the domain blacklisted from their ability to deliver their own official Facebook email notifications. There probably ought to be better ways to do that, but the fact Facebook went “yeah, we gotta register the shitty domain facebookemail.com” makes me think they’re working around a crappy limitation of smtp email.
There ought to be no limitation with, say, email.facebook.com. Sure, have the domain facebookemail to prevent bad actors grabbing it, but only use it as a redirection.
I don’t think there’s mail server software in existence that would choke on a subdomain like that. There might be a few mail admins too easily confused to be able to set it up, but I doubt there are any of those at Facebook.
That said, most people aren’t going know that a subdomain is safer than a legitimate looking alternative, so maybe it’s all moot.
Tangentially, it seems that someone has squatted on facebook-email.com (note the hyphen), so I expect that Zuck’s lawyers are crawling all over whoever’s done that.
I’m not up to speed on exactly how spam filters blacklist domains but I strongly suspect if Gmail thought spam was coming from email.facebook.com then it would restrict facebook.com too. That’s the only reason I can think of for creating such a clunky domain; it’s that a neater looking sub domain won’t avoid the problem - hence having to register something completely different.
That sounds like a preference that would be added by whoever configured the server rather than anything else. I’ve definitely seen situations where a third-level domain has been under the control of (or sold to) a third party and so it wouldn’t make sense to block the second-level, or other third-levels branched off from it if only one third-level misbehaved. Edit: And I don’t just mean countries that treat second-level as top-level for some uses, like, say .co.uk.
I have no idea what the defaults are for various automatic spam blockers, since both arguments have merit.
It’s been a while since I’ve been in tech. Is there any kind of DNS reason why you’d want email coming from a different domain? Like to skip steps in DNS resolution by going straight to a domain name instead of resolving a subdomain to the main domain?
A lot of things that don’t make sense 99.9% of the time make sense at the scale of Google and Facebook. Whether this is one, I can’t say.
Technically, it might be faster, but that’s not usually the reason. Email servers generally have to do a lot of work to confirm email messages are not spam. That work usually takes significantly longer than any potential DNS savings. In fact, that spam checking is probably the reason you see the secondary domains used.
When the main domain used for many purposes (like servers, users, printers, vendor communications, accounting communications, and so forth) It leaves a lot of room for misuse. Many pre-ransomware viruses would just send out thousands of emails iper hour. The mass communicating server could also reduce the domain reputation. There are just so many ways to tarnish the reputation of your email server or your email domain.
Many spam analysis systems group the subdomains and domain together. The subdomains contribute to the domain score and the domain score contributes to the subdomain score. To send a lot of emails successfully, you need both your servers and domains to have a very strong and very good reputation. Any marks on that reputation might prevent emails from being received by users. When large numbers of emails need to be controlled, it can be hard to get everyone in the organization to adhere to email rules (especially when the the problems aren’t users, but viruses/hackers) and easy to just register a new domain, more strictly controlled domain.
Some of the recent changes in email policies/tech might change the game, but old habits die hard. Separate domains can still generally be more successfully delivered, have potential security benefits, and can often work around IT or policy restrictions. They might phase out, but they might not. The benefit usually outweighs the slight disadvantage that 99% of people won’t see.
tl;dr
Better controlled email reputation.
Congratulations, you belong to the 3% of users who know what a domain is and why that matters. Everyone else uses Google (or DuckDuckGo because “Google bad”) to search for their favorite websites every time.
Google has one that is the most suspect url in existence, I don’t remember what it was but I verified it three different ways to be sure.
UPS apparently subcontracts their hiring to fucking Indonesia so you’ll get people working in a phone bank overseas asking for personal information.
Why the fuck did you click a link like that in the first place? That first message is basically screaming at you that it’s a phishing attempt.
Best opsec is to delete and block, ideally without opening it at all to avoid read receipts (if that’s a function in your phone). If you think it might be legit, go to the website on your own and find a way to confirm independently. If that’s still too much to follow through with, at the very least don’t click random links sent to you unprompted.
Hey dude, you had an opportunity to educate someone and instead you belittled them. As someone who works in cyber, please don’t do that. People get stigmatised against cyber and IT professionals and they stop trusting us. Users don’t know what we do, so be kind to them the way you should be kind to anyone learning new things. https://xkcd.com/1053/
Could someone educate me on the possible damage clicking a link can bring, assuming I’m not interacting with the website any more than that?
Not doubting there’s damage, just curious. I’d think they’d get some maybe usable info from fingerprinting or something? Could javascripts lead to more serious problems?
If you do nothing but click the link and then close the resulting website without clicking anything else, all that will happen is that they’ll know you’re someone who clicks such links and you’re likely to get more of them.
The least it wil do is confirm your email to be in use for further scams.
There could theoretically be a vulnerability in your browser that would allow them to infect you with viruses, but such vulnerabilities are much much more valuable used elsewhere (or cashed in through security research bounties). One I’ve seen is that the page further phishes you into downloading and installing an “update” to your browser that’s really a virus, or they simply try to phish you out of money, for example by asking you to pay the shipping costs again.
It’s also a way to build lists of who actually clicks the links, that they resell to the next sucker (scamming is suckers all the way down, they all buy The Next Big Technique from some guy), ensuring you will get further spam in the future.
There’s actually a fun technique to do to avoid further spams when it comes to voice calls. A little know fact is that elevator call buttons are actually just phones that have a phone number, and if you dial the number, it will automatically answer and you will hear whatever is in the elevator (generally nothing). If you pick up but don’t say a word, their automated systems will flag you as an elevator phone number and they will stop calling in order to stop wasting resources on calling numbers that won’t lead to money.
I got one of these today too.
Something tells me the USPS wouldn’t be using bit.ly.
100% a scam.
The USPS won’t text you, they’ll leave you a notice in your mail box. They’re the only people besides you allowed to open your mailbox legally so it’s their best avenue.
Well, they claim they couldn’t find your house. So that wouldn’t be an option. Still a scam though
They can’t find your house, but somehow they know your phone number…? I don’t know about you, but I’ve never had to use a person’s email address or phone number when I was mailing them a letter or package, just their physical address or post office box.
deleted by creator
Expecting them to have my phone number but not my address is a mental leap I cannot fathom in the first place.
I think there’s now a generation gap between kids today and people who were routinely sent to tubgirl and goatse during the internet’s formal years.
If your URL is fucky, it’s a scam. If you clicked one, they’ll send you more.
Our parents couldn’t use computers properly, and now our kids can’t use them properly either.
That being said, I learned the hard way back in the golden age many, many times.
The good old days of Azureus and Limewire
You clicked a random link from an sms message?
That’s a bold move, Cotton.
Bruh, just look at the address bar. That is not a USPS domain. Obviously it’s a scam.
- 3rd party URL shortener, immediate red flag
- Non-USPS.com domain once you tapped it (which you shouldn’t have)
- National service sending from a South Carolina area code instead of a short code or a toll free number
- Does USPS even have your phone number tied to your delivery address?
That also doesn’t look anything like a USPS tracking number (which, if this were real, you’d probably already have). Pro-tip: USPS has “informed delivery” where they’ll send you an email every day with scans of your mail and any packages on their way to you. Which would give you another way to know that this isn’t real.
PSA you can check a bitly link without clicking it by using their link checker: https://support.bitly.com/hc/en-us/p/link-checker
TIL, ty
Look at the URL. Of course it’s a scam.
Go to the official UPS website (do not click that link, google it) and enter your tracking number.
If you don’t have a tracking number it means you didn’t order anything, and it’s certainly a scam.This is usps, not ups, but everything else is accurate.
Always check the real site without using a link to get there.
Report this at https://reportfraud.ftc.gov/.
Also, because they’re using Bitly for URL obfuscation report it to them at https://bitly.com/pages/trust/report-abuse.
For any of the fake domains you run into report it to both the registrar of the domain as well as the owner of the actual IP address it points to.
Aside from all of the red flags already listed in other comments…are you even expecting a package to be delivered? I almost never receive a package that I don’t expect